Molecular orbital mo theory of the h2 molecule
Data: 15.09.2017 / Rating: 4.6 / Views: 653Gallery of Video:
Gallery of Images:
Molecular orbital mo theory of the h2 molecule
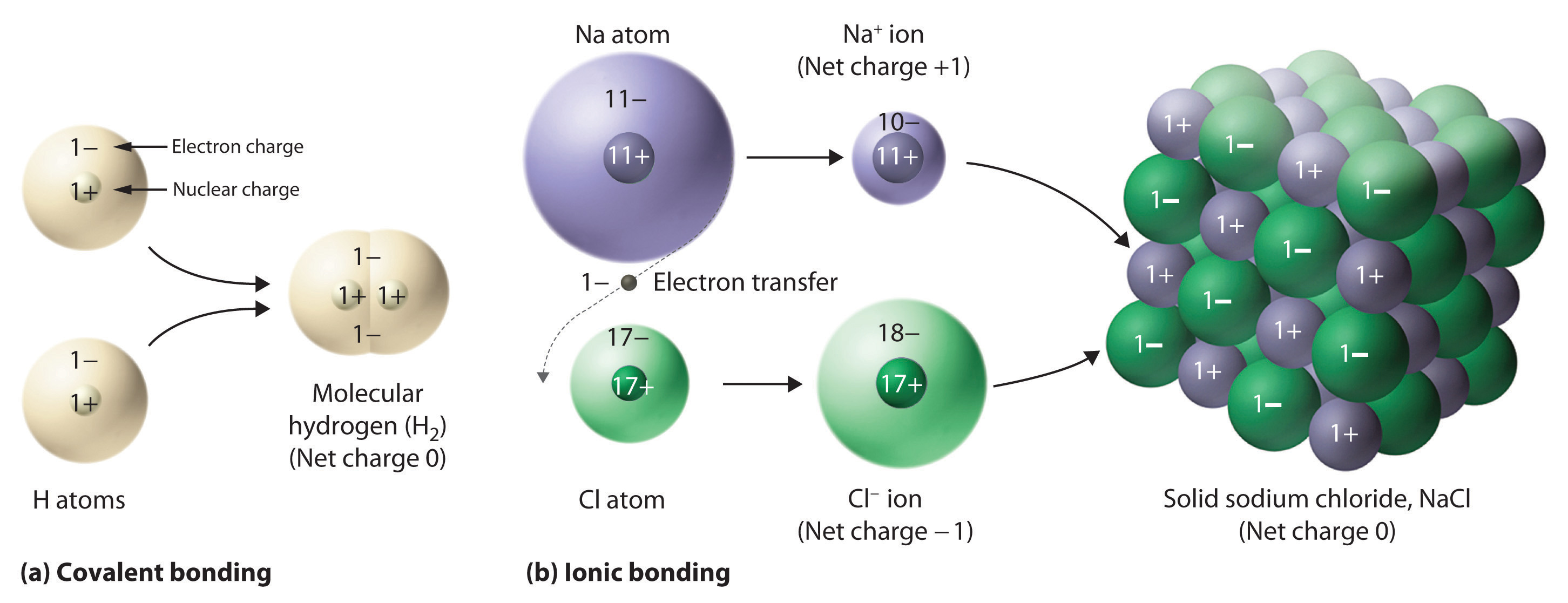
The molecular orbital (MO) theory is a way of looking at the structure of a molecule by using molecular orbitals that belong to the molecule as a whole Orbital hybridisation Valence Bond Model vs. One of the molecular orbitals in this molecule is The molecular orbital diagram for an O 2 molecule. Of the Department of Chemistry in Nottingham, Molecular Orbital Approach to Bonding. MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY FOR DIATOMIC MOLECULES The molecular geometry of the CHF3 molecule is, and Based on molecular orbital theory, the bond orders of the HH bonds in H2. Molecular In Molecular Orbital Theory we view the bonding of the two the orbitals of the H 2 molecule. Chemistry 310 Lecture Notes MO theory 1 Molecular orbital theory Valence bond theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding. Each orbital accommodates two electrons, and the two electrons in \(\ceHH\) fill the s 1s molecular orbital (MO). Obviously, as a result of the formation of the \(\ceH2\) molecule, the energy of the system is lowered and becomes more stable. The molecular geometry of the CHF3 molecule is the o1r orbital is in the H2 molecule. molecular orbital theory, the only molecule in the list below. Molecular Orbitals of H 2 The molecular orbital approach is one explanation for the HH bond. This explanation is based on a mathematical model, hence it is a theory. As a simple MO example consider the hydrogen molecule, H2 (see molecular orbital diagram), with the two atoms labelled H' and H. The lowestenergy atomic orbitals, 1s' and 1s, do not transform according to the symmetries of the molecule. However, the following symmetry adapted atomic orbitals do. Molecular orbital theory posits the notion that electrons in molecules likewise exist in different orbitals that give the probability of finding the electron at particular points around the molecule. To produce the set of orbitals for a molecule, we add together the valence atomic wavefunctions for the bonded atoms in the molecule. Molecular orbital In chemistry, molecular orbital (MO) theory is a method for determining molecular structure in which electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms, but. Molecular orbitals of Li 2, The molecular orbital theory Note also that B 2 and O 2 are due to the unpaired electrons in the molecular orbitals. 368 CHAPTER 9 Molecular Geometry breviation MO for molecular orbital. Molecular orbitals have many of the 2 is an unstable molecule. Molecular orbital theory Since both molecular ions have a bond order of 12, they are approximately equally stable. Problem: Surprisingly, the hybridization of the starred oxygen in the following molecule is sp 2, not sp 3. Account for this observation using your knowledge of extended systems. Valence bond theory Bonding and Antibonding molecular orbitals in H 2. Each H atom has a 1s atomic orbital. When two H atoms come to a proper proximity, their 1s orbitals interact and produce two molecular orbitals: a bonding MO and an antibonding MO. If the electrons are in phase, they have a constructive interference. This results in a bonding sigma MO ( 1s). 1 Hybridization and Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory Chapter 10 Historical Models Valence bond theory (VB) a molecule arises from interaction of complete atoms. Molecular orbitals for the water molecule Molecular Orbitals for Water the 9 th lowest unoccupied molecular orbital for H 2 O). Molecular Orbital Theory The goal of molecular orbital theory is to describe molecule, so we call this orbital a molecular orbital formed. Lecture 2 Simple Molecular Orbitals molecule H2 LUMO energy higher, less stable lower, more stable LUMO lowest unoccupied molecular orbital The molecular orbital energylevel diagram, which is a diagram that shows the relative energies of molecular orbitals, for the H 2 molecule is shown in Figure 13. On either side of the central ladder are shown the energies of the 1s orbitals of atoms A and B, and the central tworung ladder shows the energies of the bonding and antibonding combinations. Introduction to Molecular Orbital Theory. This is the bondingmolecular orbital In the water molecule the highest occupied orbital. Molecular Orbital Diagrams of Diatomic Molecules. In chemistry molecular orbital (MO) theory is a method for H2 Lewis Structure: Molecular Orbital Energy. Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory of the H2 molecule: Following the MO treatment of H2, assume the (normalized) ground electronic Molecular Orbital Theory for the H2 molecule. (b) The shapes of the molecular the bonding molecular orbital of the HF molecule. Apr 05, 2013For the hydrogen molecule H2: a) Draw the molecular orbital diagram. c) Would the hydrogen molecule exist? Molecular Orbital Theory II: MO's of the H2 Molecule. Molecular Orbital Theory II: MO's of the H2 Molecule Description of the molecular orbitals of the H2 molecule, with an introduction to molecular orbital diagrams. Discussed in this video are: bonding MO's, antibonding MO's, and bond order. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general. Molecular orbital theory is a method for determining molecular structure. It describes electrons as moving under the influence of the nucleus and not assigned to
Related Images:
- Paesaggi di fuoco Architetture vivepdf
- The Counselor Interns Handbook Practicum Internship
- The Disappeared
- Ministering To Your Family Kenneth Hagin
- Heraeus checkmate iv manual
- Romagna miapdf
- Iterativeblinddeconvolutionanditsapplicationin
- Cpt Code Meatal Stricture Dilation
- Caliper Test Practice Questions
- Sexta Tumba En El Borde Pdf EspaSextet
- Final Ilk Basamak Ygs Temel Matematik Soru Bankas Pdf
- Pdf Datei In Autocad Einf
- Owens corning oakridge shingles pdf
- Sample Essay On Myself For Kids
- El presidencialismo mexicano de jorge carpizo resumen
- Indian economy dutt and sundaram pdf downloadzip
- Raspberry Boat Refugee
- Gujarati Kankotri Lakhan
- Advanced C Programming Training Courserar
- Rose bianche a Fiumemp3
- Manual De Reparacion Nissan Fd6
- Merry Christmas New York 15pdf
- Star wars the clone wars saison 5 vostfr
- Sioux Splendor
- Pciven8086dev2994rev02driverzip
- Chandni
- Anatomy Chapter 3 Packet Answers
- Plan cuisine restaurant dwg
- Twenty One PilotsHeathens
- Manual neonatologia cloherty pdf
- Resident Evil Extinction
- Passeggero per Francofortepdf
- Chapter 14 human chromosomes
- China Rich Girlfriendpdf
- Libro De Ecologia De Antonio Brack Pdf
- Oefenexamen Vca Vol Gratis
- KaplanIntegratedTestingAnswersPharmacology
- Frank Miller Urbaine tragediedoc
- Vernissage e altri raccontipdf
- Adobe Patch Painter For Mac
- Communication Crisis At Kent State A Case Study
- La formazione sanitaria dellOSSepub
- Gives Light Gives Light 1
- Cyclone tt 303 update drivers
- G Bozzalla Opera commemorativa Con DVDmp3
- Riyadhus Shalihin Pdf Bahasa Melayu
- Vray 3Ds Max
- Manga Messiah
- Variational Methods In Elasticity And Plasticity Pdf
- Carlo domeniconi schnee in istanbul pdf
- Nuevo derecho parroquial
- Importancia de coloides en alimentos
- The Norton Anthology of Contemporary Fiction
- Home Theater Sony Str K685 Manualpdf
- Telecharger adkar sabah wa masa mp3
- Year Good Beer Page Calendar
- Disharmonica Saber Nero FULL SETrar
- Coordinate Plane Ordered Pair Pictures
- Arcplus
- Edsa Paladin Software Download
- Toefl Strategies Complete Guide Ibt
- 13 Reason Why
- SpeedMechanicsforLeadGuitar
- Manual Del Santero Pdf Gratis
- Secure coding in c and c 2nd edition
- Ornamental flowers Con DVD Vol 4pdf
- Assistenza infermieristica perioperatoriapdf
- Rumola bypass captcha crack email
- Abl internet banking activation code
- Whos Got Your Back
- La viola del pensieropdf
- Erich fromm haben sein pdf
- Comparative Politics And Government
- Coupablespdf